One of the most common and universal machine tools in the manufacturing and mechanical engineering field is a lathe machine. The lathe is known as the mother of all machine tools because it is critical in the production of raw materials to accurate and useful parts. Lathe machines have played a leading role in production engineering and industrial production since a traditional workshop up to modern CNC facilities.
This is a complete manual that covers all information about lathe machines such as definition, working principle, parts, types, specifications, benefits, and some real-world applications. It is particularly handy among students and professionals whose major is Mechanical Engineering, Manufacturing Process and Production Engineering.
What is a Lathe Machine?
A lathe machine is a machine that is mostly employed to take away material on a rotating piece of work so as to get the required shape and size. The fundamental mechanism that works is that the work piece is rotated against a fixed cutting tool which is slowly fed into the material to carry out machining processes.
Lathe machines find extensive application when making cylindrical, conical and symmetrical parts. Examples of these common operations on a lathe include turning, facing, drilling, threading, knurling, grooving and boring. Since lathe machines are more specific and multiple in multiplicity, the subject is fundamental in the study of Engineering Basics and Workshop Machinery.
Main Parts of a Lathe Machine
There are various important parts of a lathe machine that help to maintain the machine as an accurate and steady machining machine.
- The bed forms the hard foundation of the lathe, and is commonly composed of cast iron. It aids in the support of the other components and the correct alignment of the process of machining.
- The spindle, the speed control mechanism and the gear setup to move the work piece are placed at the headstock, which is the part at the left side of the bed.
- The tailstock that is on the right side supports the free end of the work piece and it may also carry tools like drills and reamers.
- The carriage runs across the bed and carries the cutting tool. It consists of saddle, cross slide, compound rest and tool post which gives an opportunity to control the tool movement in the most accurate way.
- The feed is automatically fed and the thread cut with precision through the lead screw and feed rod.
- The work piece is firmly clamped with the help of the chuck. The most common ones are 3-jaw self-centring chucks as well as 4-jaw independent chucks.
- The apron on the front of the carriage has gears and levers which work longitudinal and cross feeds.

Common Operations Performed on a Lathe Machine
The lathe machines can be used to carry out a very high number of machining functions, and that is why they are highly versatile within the Manufacturing Processes.
- Turning is applied in shrinking a workpiece in diameter.
- Smoothing and flattening the end-surface.
- Threading can form internal or external screw threads.
- Drilling involves the creation of holes with the help of drill bits.
- Knurling creates a textured surface to make it easier to hold.
- The finished component is separated by parting or cutting off.
- Boring also enlarges the holes that are already in place with a high precision.
Types of Lathe Machines
A variety of lathe machines is meant to suit certain production needs.
The most used and which is applicable in general-purpose machining is the engine lathe (centre lathe).
- The turret lathe enables a rapid change of tools and is suitable in mass production and repetitive processes.
- Computer numerical control is used in the CNC lathe to provide highly accurate, automated and high volume production. Modern CNC Lathe systems and advanced manufacturing require the use of CNC lathe machines.
- The bench lathe is compact and small and it is mostly utilized in light-duty and educational purposes.
- The tool room lathe is also the accuracy work tool which is more accurate in work and also has more control of speed.
- The capstan lathe has been a lighter version of the turret lathe, much used in small to medium batch production.
- The speed lathe is simple in construction without a gearbox and is normally applied in woodturning, polishing and spinning.
Specifications of a Lathe Machine
In choosing a lathe machine, a number of specifications should be put into consideration in order to make sure that it fits a certain job.
These are the swing over bed that means what is the maximum diameter of the work piece and the distance between centres and that is the maximum length of material that could be mounted. Additional details of great importance include the range of spindle speed, length of bed, the size of spindle bore and horsepower of the motor, which determines the size of machine and performance.
Advantages of Using a Lathe Machine
Lathe machines have a great number of benefits in the sphere of Machine Tools and manufacturing.
They are very versatile as they can carry out several operations on one machine. Lathe machines are very precise and repeatable and this guarantees the same quality of production. The CNC lathe machines greatly save time and human error during machining due to automation. Moreover, lathe machines have got the capability of operating on a diverse selection of materials, which include metals, plastics, wood and composite.

Applications of Lathe Machines
Lathe machines have a vast number of industries where they can be used.
They produce shafts, pistons, bushings and engine parts in the automotive sector. Lathe machines are used in aerospace to make lightweight and high-precision components. Nuts and bolts, gears, and flanges are manufactured by using the metalworking and fabrication industry and lathes. They find application in the medical industry to make surgical instruments and implants. Woodworking, maintenance shops and repair shops are also common places where lathe machines are utilized.
Final Thoughts
The lathe machine remains one of the pillars of the modern manufacturing production combining the time-honored concepts of machining with the latest automation systems. Its capability to form materials precisely and effectively does not need to be addressed whether as a manual centre lathe in a workshop or a CNC lathe in a production line.
Any person studying or employed in the field of Mechanical Engineering, Workshop Machinery, or Production Engineering would need to have knowledge of the lathe machines, and how to maximize the manufacturing process and how to produce high-quality components.




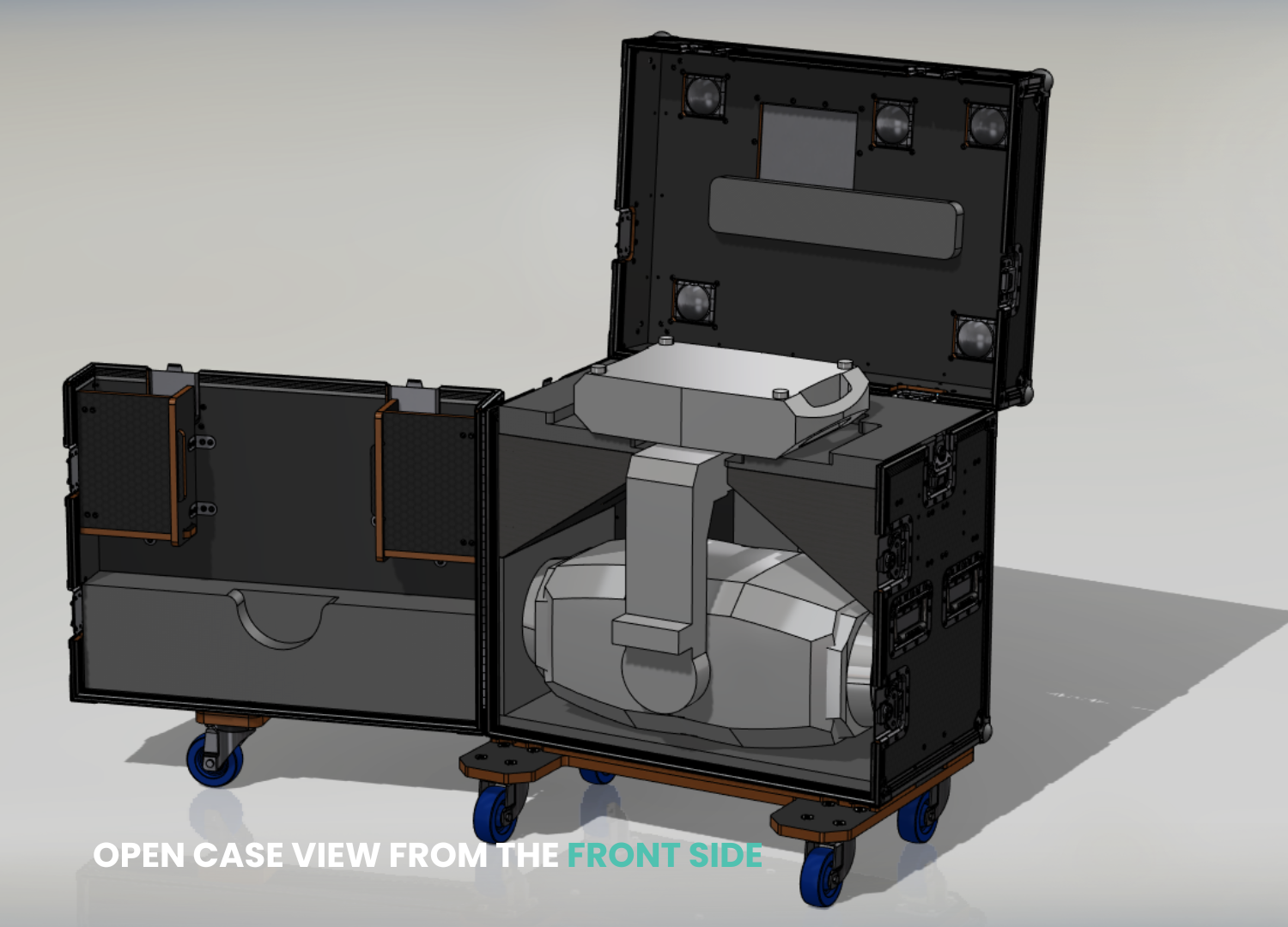








 ; paid such as PowerInspect, to do inspection.
; paid such as PowerInspect, to do inspection.